Helping with Dystonia
- Mariana Barreto
- Mar 12, 2021
- 2 min read
Updated: Aug 21, 2024
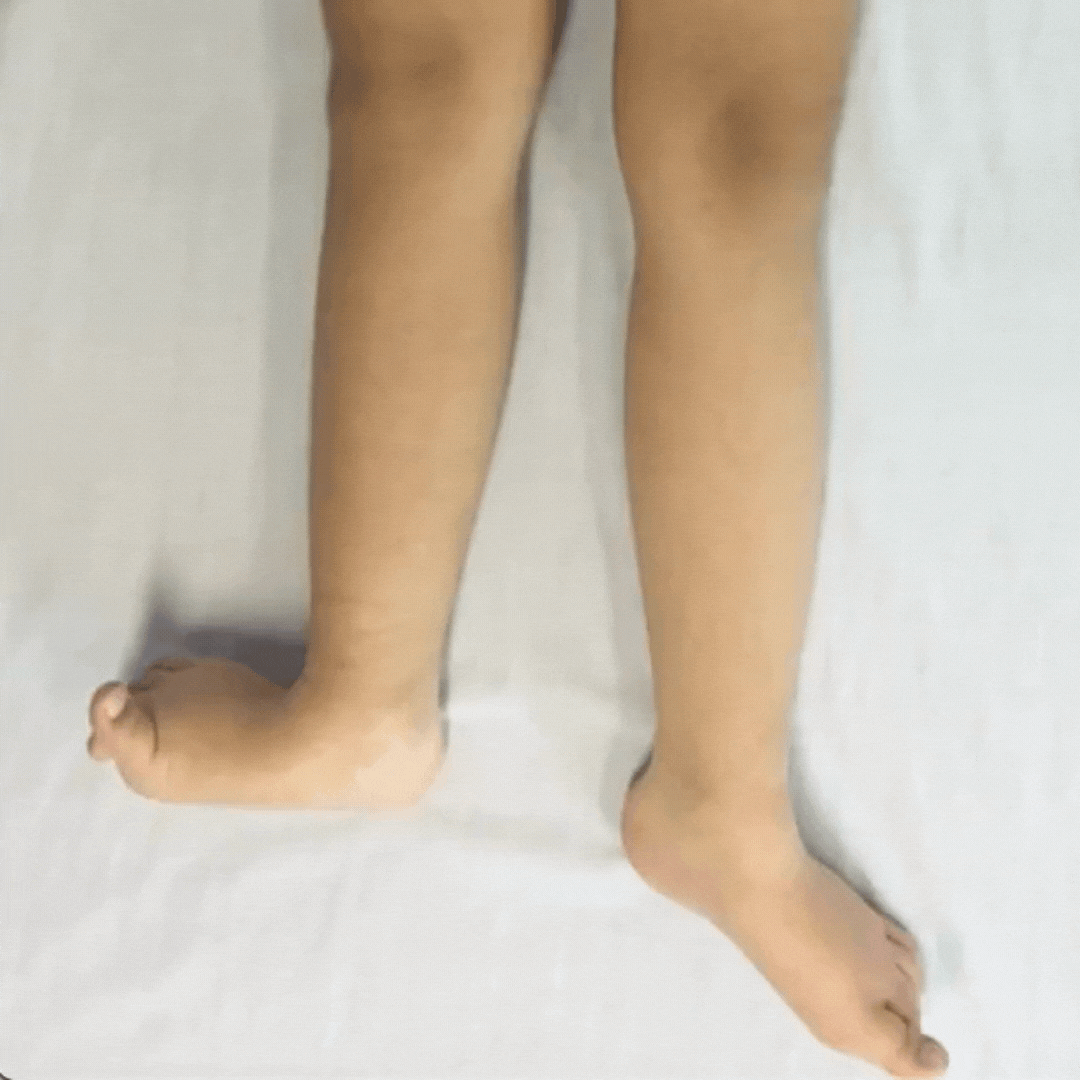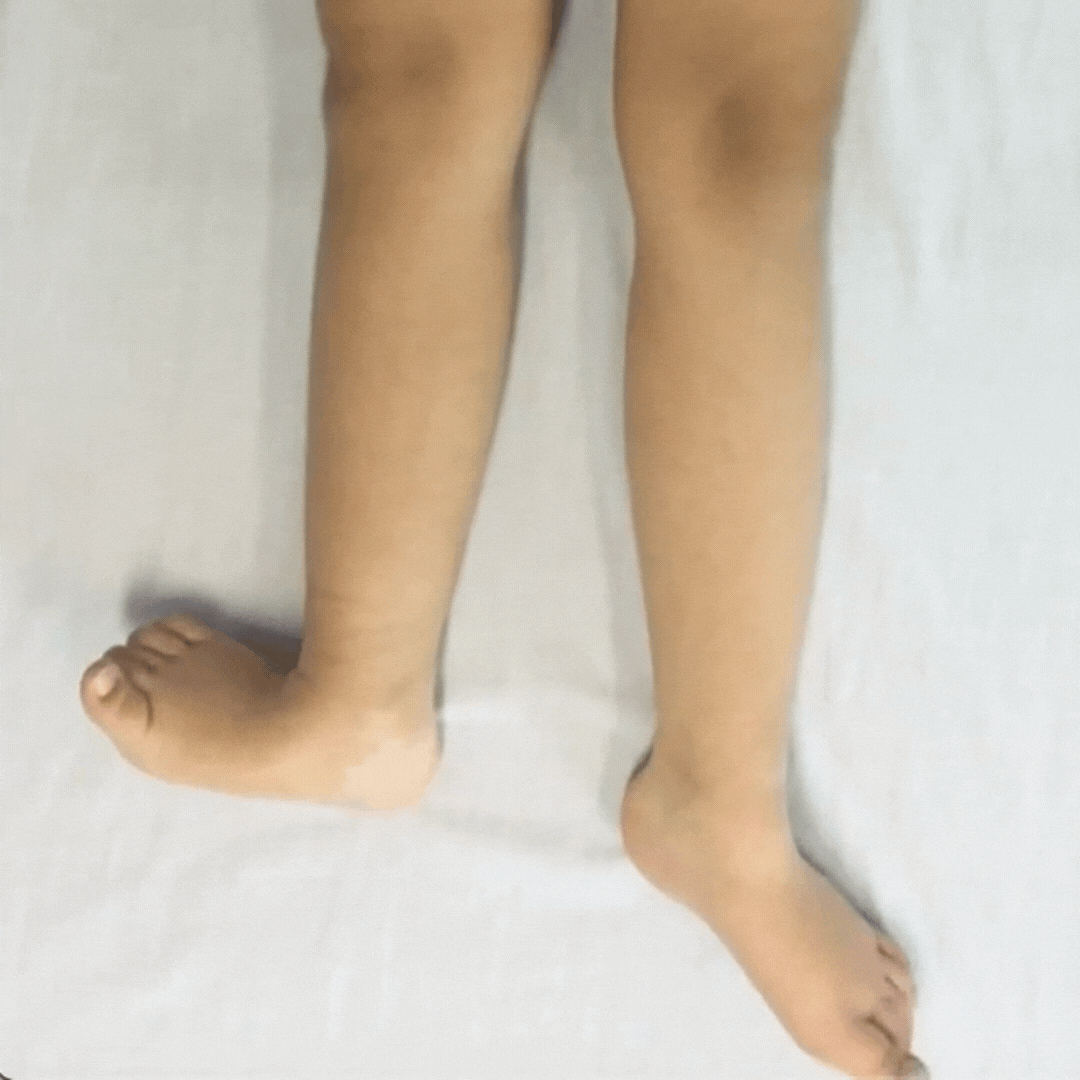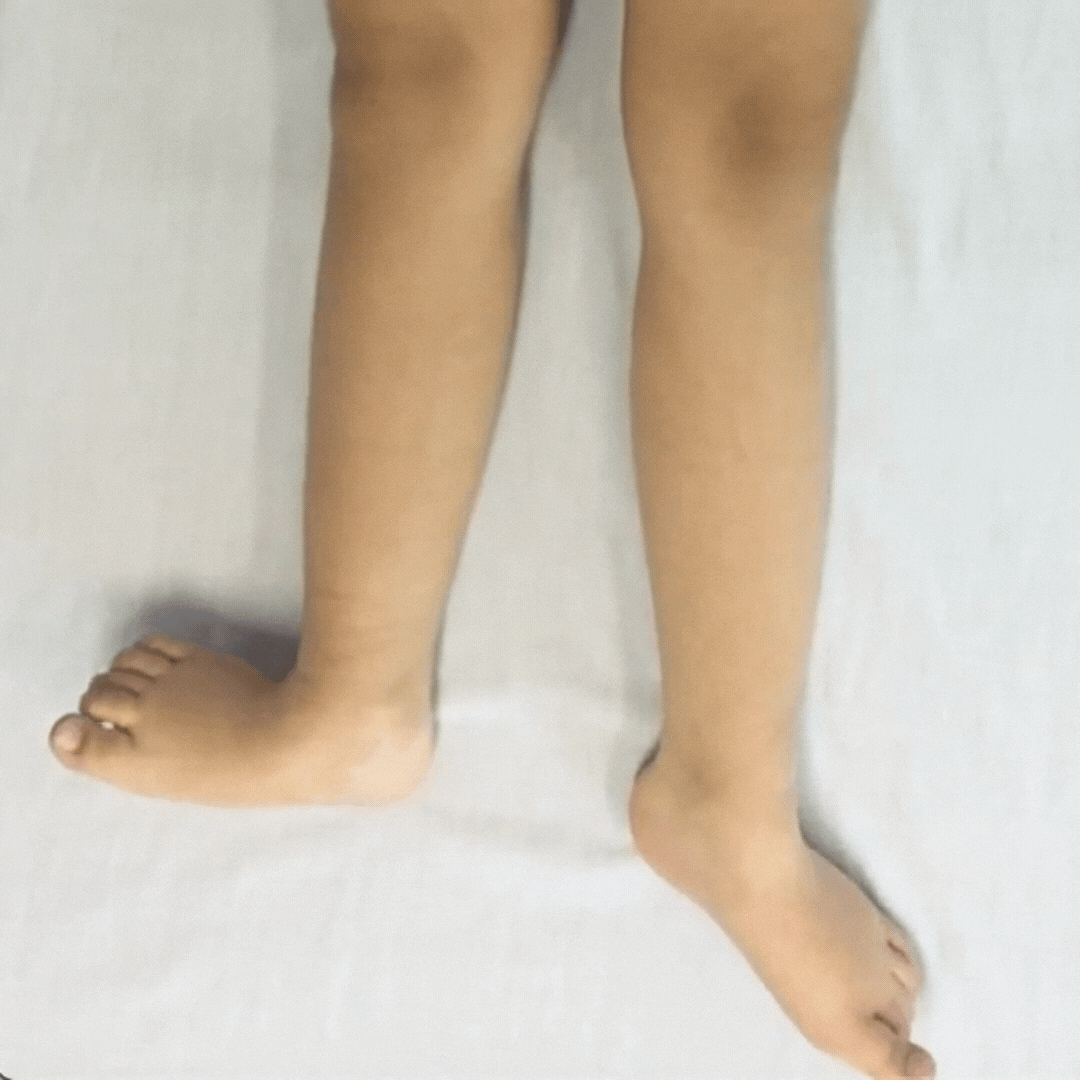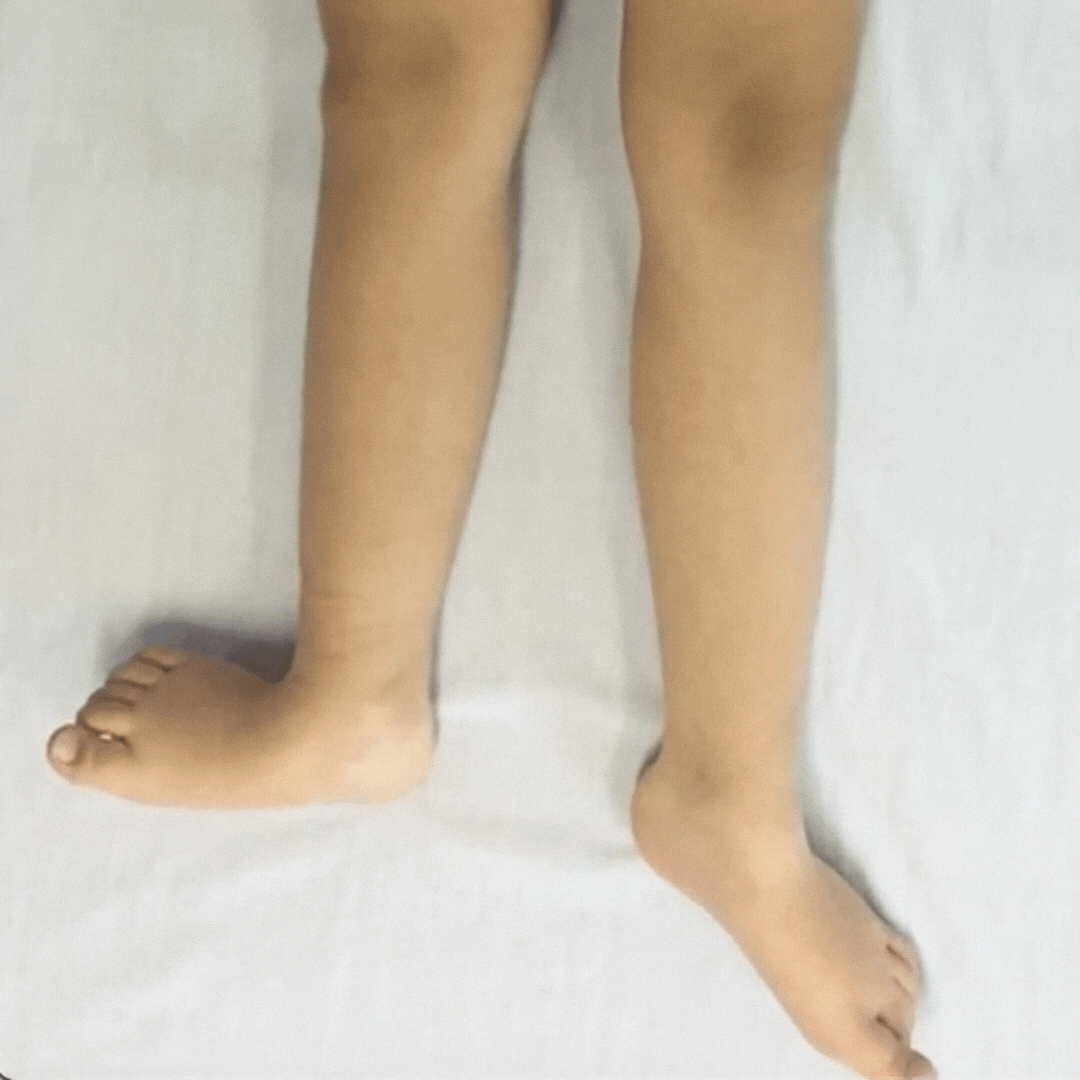
Children with dystonia have difficulties controlling movements as their muscle tone fluctuates, it varies moment-to-moment.
Dystonia is described as a movement disorder in which intermittent muscle contractions cause repetitive movements and abnormal postures.
Understanding how muscle tone is regulated and the role fascia plays in this regulation help us design strategies to help the child. We revisited these mechanisms previously in this post. The key concept to consider is the fact that fascia is richly innervated and it is considered the organ of proprioception* **.
In other words fascia plays an important role in how we feel our bodies and in muscle tone regulation.
There are two main ideas we have in mind while helping kids with dystonia:
Daily fascia therapy done by the parents helps with tone regulation. Our techniques improve the tension (the needed tension) in the fascial system. Having the right tension will help with the stability of the receptors that are fundamental for muscle tone regulation.
External wrapping (like the binder and wraps) and our ideas to play help organize the sensory system of the child bringing more control of the muscle tone.

When the child’s fascia gets more organized, the child gets calmer, there are less involuntary contractions. This is the first step to develop more accuracy in their fine motor skills and improve functionality.
To start doing fascia therapy with your child, learn the first exercise to improve torso control here.


Comments